Manitoba, located in the heart of Canada, is bordered by Saskatchewan to the west, Ontario to the east, and the United States to the south (North Dakota and Minnesota). With a population of approximately 1.4 million, it boasts a rich cultural heritage shaped by Indigenous traditions and the influences of immigrant communities. The capital city, Winnipeg, is not only the largest urban center in the province but also a vibrant cultural hub known for events such as Folklorama, North America’s largest multicultural festival.
Primary industries that sustain the province include agriculture, aerospace, energy, forestry, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing. The variety of industries contributes towards a lower cost of living in comparison to other provinces. Manitoba boasts a varied landscape. The Hudson Bay coastline and expansive Arctic tundra bordering the province in the north, with boreal forests as one moves towards the south. The central region of Manitoba is dominated by fertile prairie grasslands.
Real Estate
A majority of the population of Manitoba resides in Winnipeg. Therefore, Winnipeg is major directing force in the real estate trends and preferences for the Province. The real estate market in Manitoba has seen significant changes in recent years. The province is currently experiencing a strong seller’s market, driven by low inventory and high demand for housing. Although, the prices have seen an increase year-over-year, the prices of real estate are still considerably lower than the national average, which makes Manitoba an optimal location for first-time home buyers and families.
Most Popular Types of properties
All options of single family homes, detached homes, condos are available throughout Manitoba. The most sought-after property types include single-family homes, condominiums, and townhouses. Single-family homes, in particular, are favored by families looking for spacious living environments. The demand for condominiums and townhouses has also increased, especially among first-time buyers and those seeking low-maintenance living
Due to majority of the population residing in urban centres, the demand for apartments remains on the rise. The most popular property types are:
- Apartments: 52%
- Single family homes: 32%
- Row residences: 10%
- Semi detached homes: 4%
The rural real estate market offers different opportunities, with properties available at lower price points. This diversity allows buyers to choose between the amenities of urban life and the tranquility of rural living.
Real Estate Trends
In April 2024, real estate sales in Manitoba surged, with a notable 23.2% increase in sales compared to the previous year. Considering that Winnipeg is a major hub for real estate activities in Manitoba, it is notable the average price of homes in Winnipeg has risen to about CAD 350,715, while the provincial average stands at approximately CAD 334,256.
These prices are significantly less than that in other provinces. Looking at the Real Estate market in Winnipeg, average prices for detached homes, attached homes and condos have all seen an increase year over year. The respective average prices for Winnipeg till September 2024 were CAD 410,000 for detached homes, CAD 361,000 for Attached homes, and CAD 277,000 for Condos. Benchmark prices in Winnipeg have increased by 4.9% since 2023.
In terms of Manitoba trends, 29% of the residents rent their homes, 69% own their homes, and 2.6% live in band housing. Besides Winnipeg, there are 9 other cities in Manitoba including Brandon, Steinbach, Winkler, and Portage la Prairie. However, all of them have a population less than 100,000.
Rural and Urban Manitoba
In Manitoba, the real estate market is defined by a clear distinction between rural and urban areas. Winnipeg, the province’s capital, is the largest urban hub, attracting the majority of residential real estate investments. It features a wide variety of housing types, including single-family homes, condos, and townhouses, making it an appealing location for first-time buyers and investors alike. Urban real estate tends to be in higher demand, particularly for newer developments near the city center. Winnipeg’s surrounding suburban areas also offer opportunities, but at a slower growth rate compared to the core city.
On the other hand, rural Manitoba presents a different real estate landscape. The properties are typically more affordable, and the demand is driven largely by agricultural, recreational, and vacation home markets. With Manitoba being a province rich in natural resources and farming, rural areas attract buyers looking for more spacious properties or those seeking land for farming or leisure purposes. Additionally, smaller cities like Brandon offer a blend of rural lifestyle with urban amenities, catering to those who want more affordable housing without compromising on some city conveniences.
Financial Considerations:
Over the past few years, mortgage rates in Manitoba have experienced significant fluctuations due to economic conditions. As of 2024, fixed mortgage rates are averaging around 4.82% for a 5-year term, while variable rates are notably higher, around 6.02% for a 5-year term.
As of September 2024, the best 1-year fixed insured mortgage rate in Manitoba is 5.65%. The best 2-year fixed insured mortgage rate is 5.34%; the best 3-year fixed insured mortgage rate in Manitoba is 4.44%; the best 5-year fixed insured mortgage rate in Manitoba is 4.19%. The best 5-year variable insured mortgage rate in Manitoba is 4.85%.
Property registration and taxes
In Manitoba, the property registration process is overseen by the province’s Land Titles Offices (LTO). When a property is purchased, a transfer of ownership must be registered at the LTO, and this is where land transfer taxes are collected. The land transfer tax is a progressive tax based on the fair market value (FMV) of the property. It starts at 0% for properties valued under $30,000 and rises to 2% for properties over $200,000. This tax must be paid when the transfer is registered, and it’s the responsibility of the buyer to cover this cost.
Property taxes in Manitoba include several components: a municipal rate, a provincial education levy, and additional local service fees. The municipal tax rate varies by locality, while the education levy is set at a standard rate across the province. Properties are assessed every two years to ensure they reflect current market values, and these assessments help determine the tax payable. Winnipeg handles its own property assessments, while the rest of the province’s properties are evaluated by the provincial offices.
More details can be found on the website of the Province of Manitoba.
Zoning & Land Use:
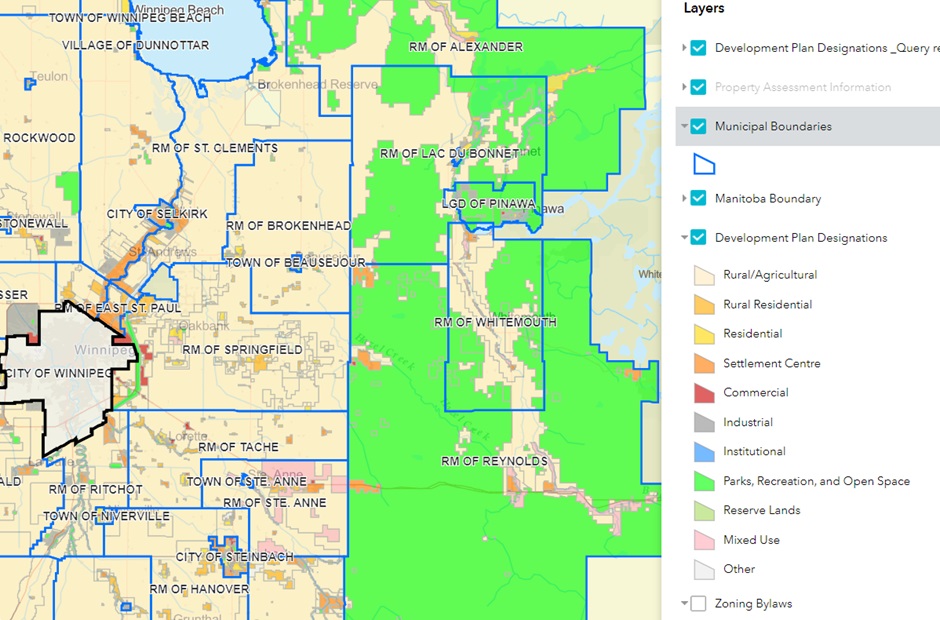
In Manitoba, zoning and land use are governed by both provincial legislation and municipal policies. These regulations control how land can be utilized, such as for residential, commercial, agricultural, or industrial purposes. Each municipality is tasked with creating its own zoning bylaws, which outline specific guidelines on property size, building types, and other development criteria. Land use planning in Manitoba often incorporates environmental factors, particularly in rural areas where agriculture dominates, to promote the sustainable use of resources. The process of approving subdivisions, issuing development permits, and rezoning land is jointly overseen by provincial and local authorities to manage both urban expansion and rural development effectively.
To understand the zoning in the entire province, check out the interactive maps on the Government of Manitoba’s Landu Use and Zoning Page.
Popular Cities




